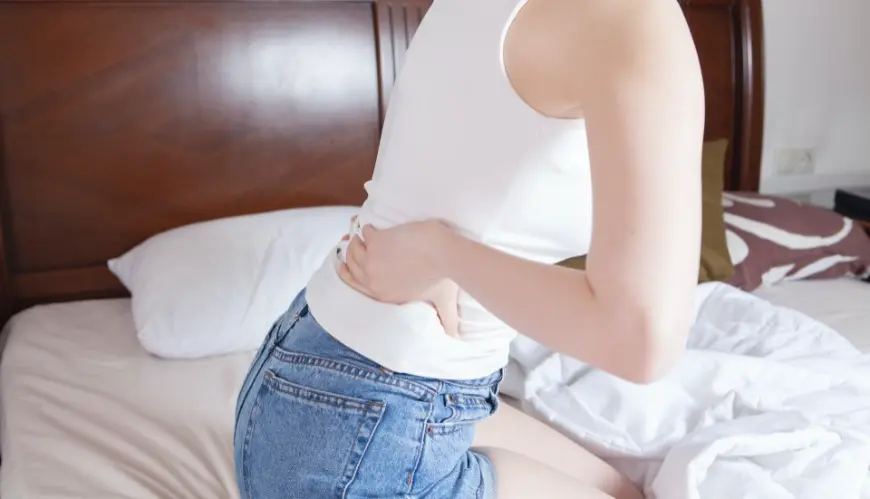
Having gas in your digestive tract is fairly common and it usually exits the body as belch or fart. However, when unable to exit, it becomes trapped. Consequently, this trapped gas can trigger back discomfort and other unpleasant symptoms.
Let's explore what prompts gaseous entrapment in your system, how to identify signs of gas-induced pain in your back, conditions that give rise to similar discomforts and methods for dealing with such pain .
Note
It's important to be aware that back pain can result from gas accumulation in your digestive tract. This typically occurs during digestion, when too much air is swallowed, or if you have an ongoing gut-related ailment. Nonetheless, remember that factors like gallstones and ulcers may also contribute to this discomfort.
What Triggers the Entrapment of Gas?
The formation and entrapment of gas may be influenced by several external and internal factors, states Dr. Neil Gupta, a distinguished associate professor in gastroenterology and a regional director for digestive health at Loyola University Medical Center based in Maywood, Illinois.
This gas, when trapped within your intestines, can precipitate discomfort or pain. The sensation could vary from severe stabbing to more subtle dull pains which usually initiates from the lower back region up towards the neck as indicated by San Ramon Urgent Care & Clinic.
"Symptoms arising due to confined gas might range from cramps to bloating centred anywhere within your gastrointestinal system," adds Dr. Gupta.
He further explains that depending on its position within your body, you may experience this discomfort at different regions as well. For instance: "If there's entrapped gas in an area of your colon located behind your stomach known as the retroperitoneum, you might suffer this pain imitating itself being positioned around upper sections of your back," mentions Dr.Gupta.
1. Air Ingestion
The primary source of pain in your back due to gas is often excessive air swallowing, explains Dr. Gupta. This could potentially cause discomfort in your upper back resulting from gas.
Ingesting a significant amount of air is the leading reason for an elevated accumulation of gas in your stomach, according to Mayo Clinic. Factors such as consuming beverages through a straw, sipping fizzy drinks like soda or beer increase the likelihood of this occurrence.
Moreover, activities such as chewing gum and taking fiber-rich diet supplements, coupled with consumption of food and drinks containing large amounts can worsen this issue.
2. The Expulsion of Gas during Digestion
Colon gas is a result of bacterial fermentation that metabolizes carbohydrates undigested by the body, specifically fiber and certain sugars and starches, Mayo Clinic suggests. Certain high-fiber foods like beans or whole grains often increase gas production as mentioned by Cleveland Clinic.
The bacteria absorb part of this resultant gas while the rest is expelled from the body in form of flatulence. According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, normal ranges between 14 to 23 instances per day.
3. Specific Persistent Health Conditions
Your consistent, intense gas pain that can be accompanied by other gut issues might not just be a regular occurrence - it could potentially indicate an underlying health issue if the aforementioned causes have been eliminated, according to Mayo Clinic.
Dr. Gupta notes any condition causing your digestive process to decelerate also increases the likelihood of amassed trapped gas; such conditions commonly include chronic constipation and others.
Persistent intestinal diseases like diverticulitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis as well as food intolerances (for example lactose- or gluten-intolerance) and small bowel bacterial overgrowth are known for leading to trapped gas. This can result in back pain – specifically lower back pain due to these resultant excessive gases dwelling within our bodies, says Mayo Clinic.
Flexures in your colon may become breeding grounds for excessive trapped gas – termed 'splenic-flexure syndrome'. According Johns Hopkins Medicine, this serious build-up of excess gases can result in discomfort from pressure buildup within the gut which often manifests through bloating symptoms supported by Intestinal Research's June 2020.
In addition, there are other persistent disorders known for causing back pains including gallbladder disease; arthritis targeting your spine and lower back regions; Chronic Pancreatitis (meaning continuous inflammation of pancreas); Peptic Ulcer Disease among many others.
Caution
Should you encounter gas discomfort along with additional symptoms such as reduced weight, diarrhea or presence of blood in stool, immediately consult your doctor to verify if it's linked to an underlying health issue.
9 Alternative Reasons for Experiencing Backache
"Although often attributed to gas, back pain can also be a sign of other more severe reasons. If you're experiencing abdominal discomfort that is manifesting as back pain, it's crucial not to overlook such symptoms," explains Dr. Gupta.
Explore the following potential explanations for your backache aside from trapped gas:
1. Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis refers to the condition of inflammation within the pancreas - an extended gland positioned in your upper abdominal area behind your stomach- which may result in back pain, as per Mayo Clinic's advice.
The following indications might reveal its presence:
- Discomfort at your upper abdomen extending towards your back
- Pain intensifying post meals
- A high body temperature
- Sensitivity across abdominal region
- Feeling nauseous
- Throwing up
- An increased heart rate
2. Gallstones
Gas is a usual cause for shoulder blade backpain, however the gallbladder issues can result in this pain too.
According to Mayo Clinic, gallstones are created when digestive fluid known as bile hardens and forms deposits within your gallbladder duct. Usually, gallstones might not cause any symptoms but when they block the duct, it can lead to several signs including:
- An intense rise of pain in upper right side or middle part of your stomach.
- Pain experienced on your right shoulder.
- The feeling of Nausea
- Throwing up
Ulcer: Cause #3
Ulcers could be a potential source of back pain. As noted by Dr. Gupta, a type of ulcer known as duodenal ulcers occur in the initial part of the small intestine and may result in:
- A burning sensation spanning from your sternum to your navel
- Back discomfort
4. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones could potentially result in both back and stomach pain, as suggested by the Mayo Clinic. Among the symptoms are:
- Intense fluctuating pain at your side and lower part of your back (beneath your ribs)
- Pain spreading into your abdomen and groin area
- Pain during urination
- An increased urge for more frequent urination or
- Urine that appears to be blood-streaked, cloudy or has a foul smell
- Feeling nauseous
- The occurrence of vomiting
- High body temperature (fever)
- Shivering from cold sensations
5. Infection in the Urinary Tract
Suffering from an infection in the urinary tract (UTI) can often cause pain in the pelvic region, lower abdomen, and back. Should this infection extend to your kidneys, it might lead to upper back pain positioned on either part of your spine according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
In addition to these pains, CDC lists other notable symptoms that come with a UTI such as:
- Discomfort or a burning sensation while passing urine
- Increased frequency of urination
- Sensation of needing to pee despite having an empty bladder
- Blood presence within urine
- Lower abdomen or groin pressure or cramping
If progression leads this into becoming a kidney related infection, you may experience added symptoms like:
- High body temperature or fever
- Cold shakes / chills
- Pain located at the side of your back or lower back pain
- Feeling nauseous leading possibly vomiting
6. Menstruation
In some individuals with uteruses, their menstrual cycle can induce signs similar to back pain instigated by gas. This usually manifests as cramps in the lower abdomen which extend towards the lumbar region.
Notably, certain individuals may face disturbances in their gastrointestinal tract (such as gas and bloating) coinciding with their monthly period according to National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD).
Other notable symptoms that could occur during menstruation include but are not limited to:
- Breast tenderness or bloating
- Strong desire for specific food items
- Irritability and mood fluctuations
- Headaches
- Feeling low on energy
Suggestion
Should you be experiencing intense period cramps with heavy menstrual flow, it is crucial to visit your doctor. This is necessary in order to exclude diagnoses like endometriosis, occurrences of ovarian cysts or other potential conditions that may present symptoms analogous to the discomfort caused by excess gas.
7. Pregnancy
Expectant individuals often experience lower back pain, particularly as their pregnancy advances. The added weight to the body's front can apply pressure on one's back and hips which leads to this phenomenon quote Johns Hopkins Medicine.
Moreover, gas-related backache also tends to occur during pregnancy due to gastrointestinal symptoms becoming prevalent at this time according to the American Pregnancy Association.
8. Chronic Pain or Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is an enduring ailment characterized by pain and tenderness throughout the body, in addition to fatigue and sleep disturbances. Its origin remains largely unexplained but it's oftentimes present amongst individuals with other chronic ailments such as depression, lupus or arthritis, according to National Institutes of Health (NIH).
People with fibromyalgia often report common areas of discomfort which include the lower back region (either side of their spine) and the upper section between their shoulder blades. This information is provided by New York Presbyterian Hospital.
9. Back Injury
Back injuries may be responsible if you are experiencing isolated back pain. The cause could range from a simple muscle pull, strain or bruising to more severe conditions such as spinal fractures or herniated disc, according to the National Library of Medicine (NLM).
The type of injury and its impact on your daily activities (e.g., inability to walk properly or lift substantial weights) might necessitate medical attention. In such cases, an X-ray examination may be recommended by your doctor as per NLM's guidelines.
The Strategies to Overcome Gas Pain Affecting Your Back
While eradicating back pain often necessitates the consistent management of a prolonged condition, there are some steps you can carry out for interim relief.
1. Consider Gas-Alleviating Medications
The discomfort of gas symptoms can often be eased with over-the-counter (OTC) medicines such as antacids, explains the Cleveland Clinic. Anti-bubbling medications like simethicone (Gas-X) are reported by Mayo Clinic to reduce gas-related unease.
In addition to these non-prescription enzyme supplements, products like Lactaid or Beano might provide relief for those struggle with digesting sugars and lactose intolerance respectively.
2. Applying warmth with a heating pad
Using warmth on your back is another way to alleviate back pains, as suggested by Mayo Clinic.
According to the University of Michigan Health, it's recommended that you heat your back using tools like a hot shower for intervals of about 15-20 minutes each time.
3. Physical Activity
It might seem odd to indulge in vigorous exercises while experiencing back discomfort; however, physical activity can foster digestion and dispel trapped gas within your digestive system as outlined by the Cleveland Clinic.
Maintaining a consistent exercise regimen can also work effectively towards prevention of subsequent accumulation of gas.
Certain specific exercises like child pose or spinal twist from yoga could be tried out too.
4. Reduce Intake of Foods and Drinks That Lead to Gas Formation
Starting your day with foods that minimize gas formation can be significant, particularly if you are easily affected by this condition.
Decreasing consumption of edibles and beverages that lead to gassiness can aid in preventing back discomfort. According to institutions like the Mayo Clinic and Cleveland Clinic, some frequent offenders are:
- Items such as beans and whole grains
- Cruciferous veggies which include cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and asparagus
- Fermented items like kombucha or kimchi
- Dairy products particularly if you're lactose intolerant
- Substitute sugars and synthetic sweeteners
While avoiding these foodstuffs isn't always feasible for nutritional reasons or otherwise yet substituting them temporarily could greatly reduce gas symptoms. Opting for alternatives such as berries, bell peppers rice or lean sources of proteins such as chicken may prove helpful.
Consultation with a Doctor
Should your backache due to gas not respond to over-the-counter solutions, or persist beyond 24 hours, a consultation with your physician is advisable. This could aid in identifying the root cause and discovering proper remedial measures.
In cases where significant symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, swooning or breathlessness accompany your back pain, an immediate call to your healthcare provider or visit to the closest emergency care center is essential.
For appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan determination, the physician might require evaluations like X-ray scans, MRI tests as well as blood exams or colonoscopies.